If you want to replace a missing or failing tooth with a state-of-the-art dental implant (watch dental implant video), your dentist will first need to make sure that you have sufficient bone in your jaw to anchor the implant. This is true no matter what type of tooth is being replaced. However, if it is an upper back tooth and there is not enough bone under the gum where the implant needs to go, the base of the implant could end up poking through an air space (located to the side of the nose) called a sinus cavity. Since you can’t anchor a dental implant to air, this presents a problem — but it is one that can often be solved with a minor in-office surgical procedure called a “sinus membrane lift.”
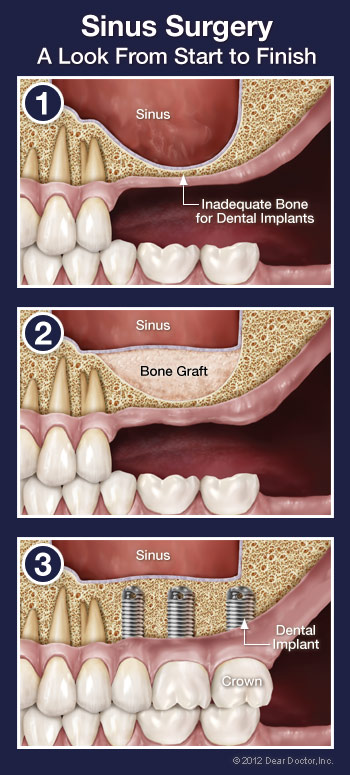
A sinus membrane lift, or sinus augmentation, involves adding bone to fill in the bottom of that air space, essentially raising the floor of the sinus cavity. Why wouldn’t there be enough bone there already? For some people, it’s simply a matter of how large their sinus cavities are, and their shape. In other cases, bone has actually been lost from the area. For example, if your tooth has been missing a long time, the bone that used to surround it may have begun to deteriorate. Bone in general needs stimulation to stay strong; in the case of the jawbone, that stimulation comes from the teeth. When teeth are lost, the bone loses stimulation and the body ceases to make new bone cells in that area. This leads to a reduction in bone volume and density. Also, if your tooth loss was due to periodontal (gum) disease, your tooth-supporting bone may have been reduced as a result of the disease. No matter what the reason is for insufficient bone, a sinus membrane lift can create more bone where it is needed.
Where does this additional bone come from? It can be bone from elsewhere in your body, such as another part of your jaw or your hip. But most often, it will be bone-grafting materials that are processed in a laboratory for these kinds of purposes. The original source may have been a human or animal donor (usually a cow). Synthetic products can also be used. All grafting materials must be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and prepared according to their guidelines. The materials are specially treated to render them completely sterile, non-contagious, and free of rejection factors. For the most part, bone grafts act as scaffolds that the body will eventually replace with its own bone.
The Procedure
Prior to scheduling surgery, your dentist will assess the shape, location, and health of the sinus using x-ray imaging. Your options for anesthesia will also be discussed. The surgery itself is usually carried out under local anesthesia by numbing the area, just as is done for a routine filling. Some people require additional sedation or anti-anxiety medication, which can either be administered orally (by mouth) or by intravenously (through a vein) via injection.
When the area has been completely numbed, an incision will be made in your gum to expose the bone that used to contain your missing tooth or teeth. A small opening will be made in the bone to reveal the membrane that lines the sinus. This membrane will be raised and the space beneath it will be filled with bone grafting material. The gum is then stitched back up. In some cases, the implant(s) can be placed directly into the grafting material before the gum is closed, eliminating the need for a second surgical procedure later on to place the implant. Often, however, the surgical site is allowed to heal for approximately 6-7 months before an implant is placed.
What to Expect After Sinus Surgery
You may experience moderate swelling and some minor discomfort that generally lasts a few days — about the same as having an upper impacted wisdom tooth removed. Sometimes a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (prescription or over-the-counter) is recommended to help minimize this. A course of antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection. If the sinus membrane becomes a bit inflamed, leading to a feeling of minor congestion, a decongestant can be helpful. If you suffer from seasonal allergies, make sure to schedule your surgery for a time when this will not be an issue.