Before prescribing any medications — even lifesaving ones, such as those used to reduce blood pressure or prevent epileptic seizures — your health care professionals carefully weigh the benefits a drug offers against the possible risks of taking it, including its potential side effects. In most cases, the side effects are relatively slight: for example, drowsiness, an upset stomach, or minor aches. But in some individuals, particular drugs may produce side effects that are more troublesome.
This is sometimes the case with a class of drugs called calcium channel blockers (CCBs), which are commonly used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and certain other heart conditions. Some people who take these medications experience a condition called gingival hyperplasia, or an overgrowth of gum tissue. This effect has also been seen in some epileptics who take an anti-seizure medication called phenytoin.
Possible Side Effects
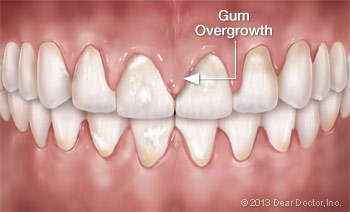
CCBs work by dilating (widening) the blood vessels, which makes it easier for the heart to pump blood. But in a small percentage of people, they also cause changes in the gums. Gum tissue may become thick and lumpy, and it may sometimes extend abnormally and start to cover the teeth. This change in appearance can cause social embarrassment, as well as discomfort and difficulty in chewing.
The overgrowth of gum tissue also makes it difficult or impossible to clean the spaces between teeth. This can cause a rapid deterioration in oral hygiene that may lead to full-blown gum disease if not treated promptly. And since poor oral hygiene is itself a contributing factor in gum overgrowth, the condition can easily spiral out of control.
In addition, some CCBs also reduce saliva flow. This may not only cause the mouth to feel dry, but may also severely reduce saliva’s protective effects on the teeth and gums.
What To Do About Gum Overgrowth
It’s always a good idea to tell your health care providers about any side effects you may be experiencing as soon as you notice them. However, even though gum tissue overgrowth may be a worrisome issue, it doesn’t mean you should stop taking your blood pressure medication! There are several options for controlling this condition, which should be discussed with all members of your medical team.
With your doctor’s consent, it may be possible for you to change your dosage or switch to a different blood pressure medication that produces fewer side effects. It can take a few months for your gums to return to normal after the change, while you are maintaining good oral hygiene at home. But even if it’s not possible for you to change your medication, there are a number of in-office treatments that can be used to help alleviate the problem.
Non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing (a type of deep cleaning) are sometimes the first step to controlling gum overgrowth. These relatively minor procedures can dramatically improve your overall oral hygiene. If necessary, they may be followed by surgical treatments to remove overgrown tissue and eliminate periodontitis — a serious condition which, if left untreated, could result in tooth loss.
In addition to regular dental cleanings, you will need to be extra vigilant at home: proper brushing technique and the use of interdental cleaners (such as floss) are needed to clean the spaces between teeth is a must. Your progress will be monitored at follow-up dental visits as needed.
While gum tissue overgrowth may seem a daunting problem, experience has shown that it can be successfully controlled by initial periodontal therapy, good at-home care, and frequent follow-up visits. Meanwhile, you should continue to follow all of your doctors’ recommendations for maintaining healthy blood pressure.

